Assembly manufacturing and Assembly installation: Optimizing production through effective processes
In the manufacture of many products, from cars and machines to electronics and household appliances, the so-called assembly is of central importance. Both the manufacture and installation are more complex than they appear at first glance. At Wacker, we are experts in assemblies and can help you with all your questions on this subject.
What are assemblies?
An assembly is basically a group of individual components or parts that are put together. They are ultimately intended to form a functional unit and are an important component of many machines, devices and systems. There are virtually no restrictions on the materials that can be used. Metal, plastic, rubber, glass or other materials are all suitable.
In industry, assemblies are often produced as individual parts and then later assembled into a larger product during final instalations. By using assemblies, manufacturers can achieve greater efficiency and better quality in production. The use of assemblies also allows production to be tailored to the specific needs of a customer or industry. Likewise, they can help minimize sources of error and improve the quality of end products
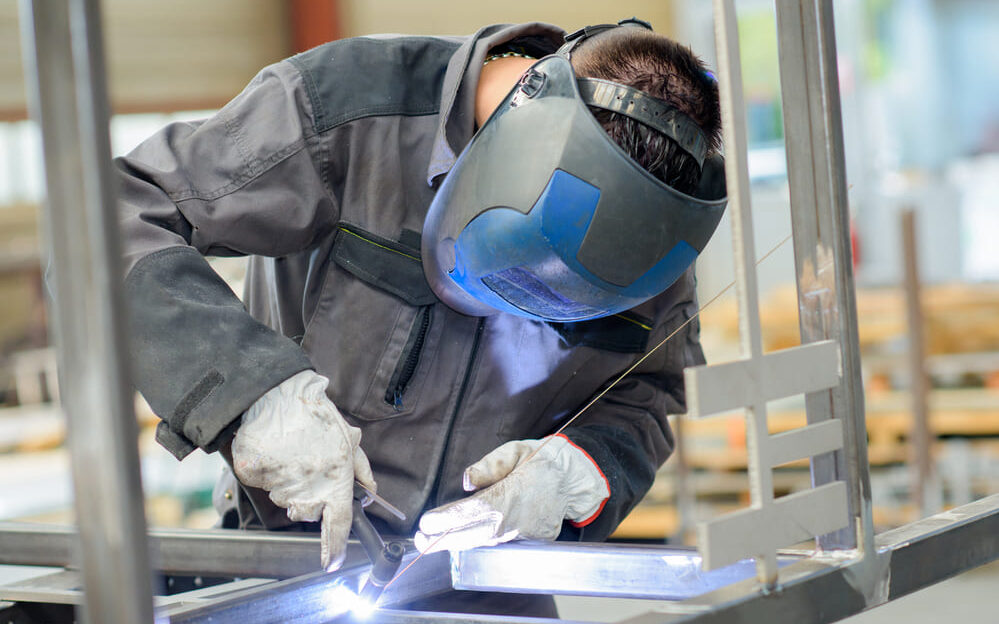

Image copyright: photography33
After the Assembly production is before the Assembly installation
Before individual parts or components can be put together into an assembly, they must first be manufactured. This takes place in the assembly manufacturing process, which can be manual or automated.
The manual manufacturing process begins with the preparation of the individual parts. Each part is checked for quality and dimensional accuracy and then machined accordingly. Then the individual parts are assembled by hand, often using adhesives, screws or soldered joints. Finally, the assembly is checked again for functionality and reworked if necessary. In contrast to manual production, the automated production of assemblies is more efficient and faster. Here, the individual parts are machined and assembled. The individual work steps are carried out by robots controlled by computer programs. This achieves high precision and consistent quality of the assemblies.
The choice between manual and automated manufacturing depends on various factors. Manual production often makes sense when small quantities or special requirements are involved. Automated production, on the other hand, is often the better choice for large quantities or high precision and quality requirements. It should be noted that in both cases, manufacturing is an important step in the production of products. Careful planning and control of the manufacturing process can save costs and improve the quality of the assemblies.
After manufacturing, the individual assemblies must be put together into a final product, which is achieved through assembly installation. Again, careful planning and control is critical to the success of the manufacturing process. The individual steps must be precisely coordinated to ensure that the assemblies and components are assembled in the correct sequence. The quality and precision of the construction assembly can be ensured by using quality control procedures such as testing or measurement.
The most important processes in component assembly
Various assembly processes are used to manufacture high-quality mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, electrical or combined systems. Depending on the technical characteristics, these are carried out either manually, partially automated or completely automated. The most important ones at a glance:
- Adjustment:
- Gluing:
- Riveting:
- Welding:
- Testing:
Adjustment is one of the upstream manufacturing steps in component assembly and is used to precisely align the components to be joined. To guarantee correct assembly, the individual components must be placed in the correct sequence, requiring maximum precision.
Bonding is used to permanently join two components together. Almost all materials can be joined and an even distribution of adhesive force can be achieved. In addition, bonding allows the production of visually appealing connections without heat stress or impairment of the material.
This process is based on the plastic deformation of a rivet after it is inserted into the rivet holes of the components to be joined. It is particularly suitable for sheet metal or parts with low thickness.
In this process, assemblies are permanently joined together by the application of localized heat (e.g. with the aid of a laser). This causes the contact surfaces of the components to melt, resulting in the materials merging into each other and thus forming a strong bond after cooling.
Testing is typically the final step in any assembly process. As part of quality assurance, it ensures that the final assembled product or assembly meets quality requirements and industry standards.
Assembly challenges
The installation of assemblies can be a complex task that requires careful planning and coordination. One of the biggest challenges is the complexity of the assemblies themselves. These often consist of many different components with different subsystems, all of which must be placed in the correct sequence and assembled in the right way. The interfaces between the assemblies must be taken into account and implemented in a professional manner. If only one part is placed or fastened incorrectly, this can lead to a malfunction of the entire assembly. A precise knowledge of the assemblies and their components is therefore essential in order to carry out the assembly successfully.
Another problem is the need to adapt to different production processes. In many cases, assemblies are produced in large quantities and used in different products. To ensure that assemblies are properly assembled in each product, they often need to be adapted to the specific requirements of different production processes.
In addition, consistent precision, concentration and a high level of technical expertise must be maintained to ensure that the assemblies function properly. Finally, the working environment is also a challenge, as in many cases the assemblies have to be assembled in confined spaces or under difficult conditions.
Overall, assembly installation requires careful planning, coordination and implementation to successfully meet the challenges. Good training of assembly workers, quality standards and effective planning of the assembly process can help overcome the challenges and achieve efficient and high-quality installation of assemblies.

Image copyright: photographee.eu